There is always a way out of a tough situation. Challenges come with any new technology that emerges, and the blockchain is no exception. But the world is on its way to finding solutions for overcoming blockchain challenges.
Blockchain technology is currently being used in both corporate and individual applications, such as banking, cryptocurrency, healthcare, and decentralized autonomous organizations. While this technology has many positive applications, it has also been the focus of numerous scams and data breaches in recent years, costing victims over $1 billion.
It’s horrible to hear that. But that’s what’s true.
In earlier blogs, we dove deeper into the challenges of blockchain and the threats that it poses in the real world. This blog will mostly talk about proposed solutions to blockchain problems, but it will also touch on blockchain challenges a little bit.
What’s the big deal about blockchain?
If implemented properly, blockchain could have magical effects.
- A blockchain is a digital ledger or database where encrypted blocks of data linked to digital assets are kept and chained together to make a reliable, permanent record of transactions.
- Distributed digital assets cannot be copied or modified once they have been sent.
- Due to their decentralized nature, digital assets can be shared, accessed transparently, and governed by a number of different parties in real-time.
- Blockchain ledgers are open and clear, and any changes are recorded. This keeps the integrity of the system and protects everyone’s interests.
- Since blockchain ledgers are public and built with data security in mind, they are a top technology for almost any industry.
Blockchain is like Google Docs but claimed to be secure.
Blockchain’s functionality can easily be compared to that of a Google Doc. A Google Doc that has been shared with numerous people is merely distributed; no copies are made or sent anywhere else. This creates a system of decentralized nodes where the main document may be accessible in real-time by everyone. Nobody has to wait for approval of their changes because they are all recorded quickly. Blockchain data and content are more secure than, say, Google Docs because they cannot be changed once they have been recorded.
Though blockchain is more complex than a Google Doc, this simplified example should help you grasp its fundamental ideas.
Real-world applications of blockchain
The blockchain has so far proven useful in the following ways:
- Role in international trade and money transfers
- Streamlining the supply chain and cutting costs
- Keeping tabs on and protecting patient information
- Having a significant impact on copyright compliance
- Protecting the nation’s identification records in the public sector
- Improving the safety of the voting process
- Important in the realm of digital currencies
- The registration and protection of all property and assets
Despite the widespread belief that blockchain-based applications are inherently more secure due to the distributed ledger technology underlying them, they have not yet proven to be a failsafe solution for protecting data from a wide variety of threats.
Blockchain has not yet become the silver bullet against vulnerable security threats.
Using Blockchain in the real world. Hope or hype?
Blockchain technology could be used in many different areas, like healthcare, banking, government, and much more. Maybe blockchain sounds like a great idea in theory, but has its actual implementation been proven to be as safe as the concept suggests?
Keep in mind, though, that blockchain technology is locked in a debate between hopeful marketing claims and more realistic criticisms. In the marketing of blockchain, it has been said that the technology is resistant to common security attacks that could hurt the privacy, integrity, and access to information that has been stored. Meanwhile, there are reasonable arguments showing that there are various ways to hack a blockchain. There is already a fully summarized list of the dangers to blockchain security and what causes them.
Undeniable facts: Blockchain technology is susceptible to security risks
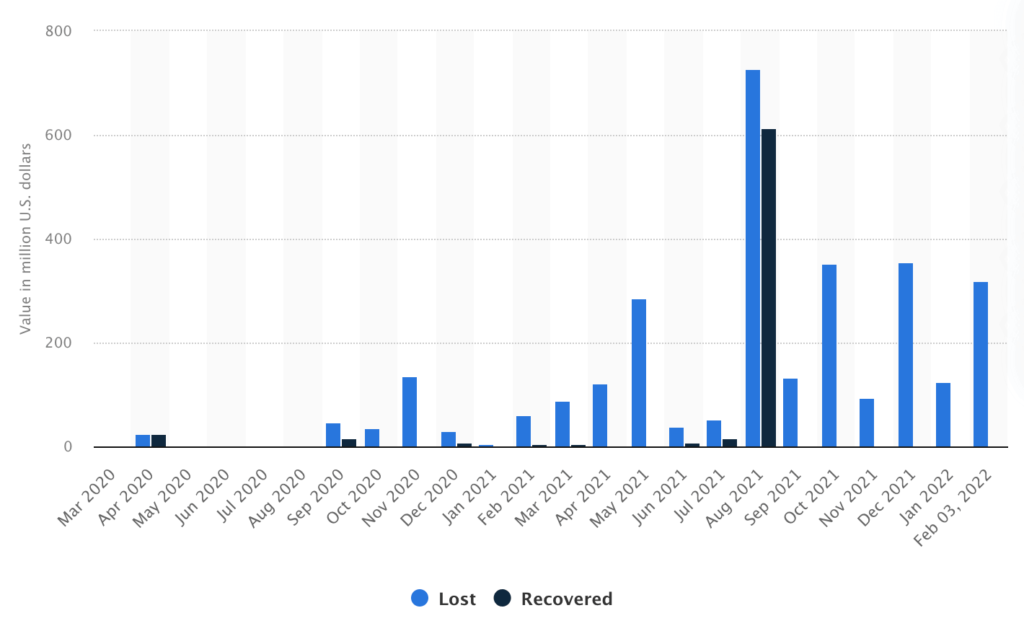
The total value of cryptocurrency lost to and recovered from theft and other attacks between March 2020 and February 2022
Out of the top 10 web application security risks listed in the well-known OWASP Top 10, a foundation that improves the security of online software, blockchain technology is subjected to 9 risks.
That’s why the security of the blockchain is critical to the development of useful blockchain applications for business.
A study conducted between 2009 and 2017 identified the major risks associated with blockchain technology.
- 51% Sheer unpredictability
- Criminal behavior
- security for personal keys
- leakage of transactional privacy
- Double-spending
- Smart contracts that are illegal
- Low-cost business practices
- Security flaws of smart contracts
- unsatisfactory smart contract
If you want to learn more about the risks and challenges associated with blockchain technology, have a look at the following articles.
- Blockchain technology risks. Is it as safe as you believe?
- Real challenges to blockchain adoption: potential issues with its implementations
- Blockchain extreme security hole: What are the biggest threats to blockchain’s authenticity
Proposed solutions for overcoming blockchain security breaches
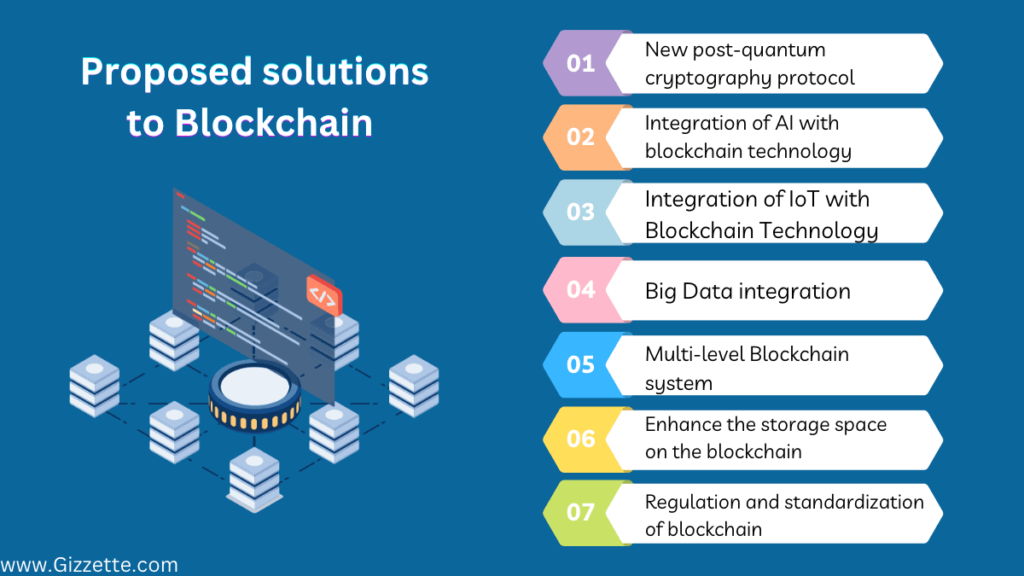
Researchers and engineers have tried a lot of different things to solve the privacy and security problems of blockchain. There have been various hypotheses put forth on the advantages of blockchain technology. let’s take a look at them.
1-New post-quantum cryptography protocol
The ECDSA technique is now in use for signing blockchain transactions. Under this technique, public keys are generated from private ones using a complex algorithm, but the process cannot be reversed. It is believed that the time needed to crack the private key is so great that it is impossible to do so.
This is known as the “post-quantum effect.” But it can be compromised, and hackers can have access to 25% of the private keys.
Because of this, researchers are working hard to create a new quantum-resistance signature method that will introduce a new post-quantum cryptography protocol.
Today, Blockchain Version 1.0 is operational, and Version 2.0 is on the horizon. It has been speculated that with the release of version 3.0, a new quantum-resistant signature algorithm will be developed.
So, there is a long way to go.
2-Integration of AI with blockchain technology
Concerns about the security of the blockchain can be dealt with in new ways. One of these is the efficient development of AI technology. Since AI is a machine, it can carry out tasks that humans would normally handle. Thus, blockchain provides a secure place to keep a lot of data, while AI generates novel scenarios and finds patterns in that data.
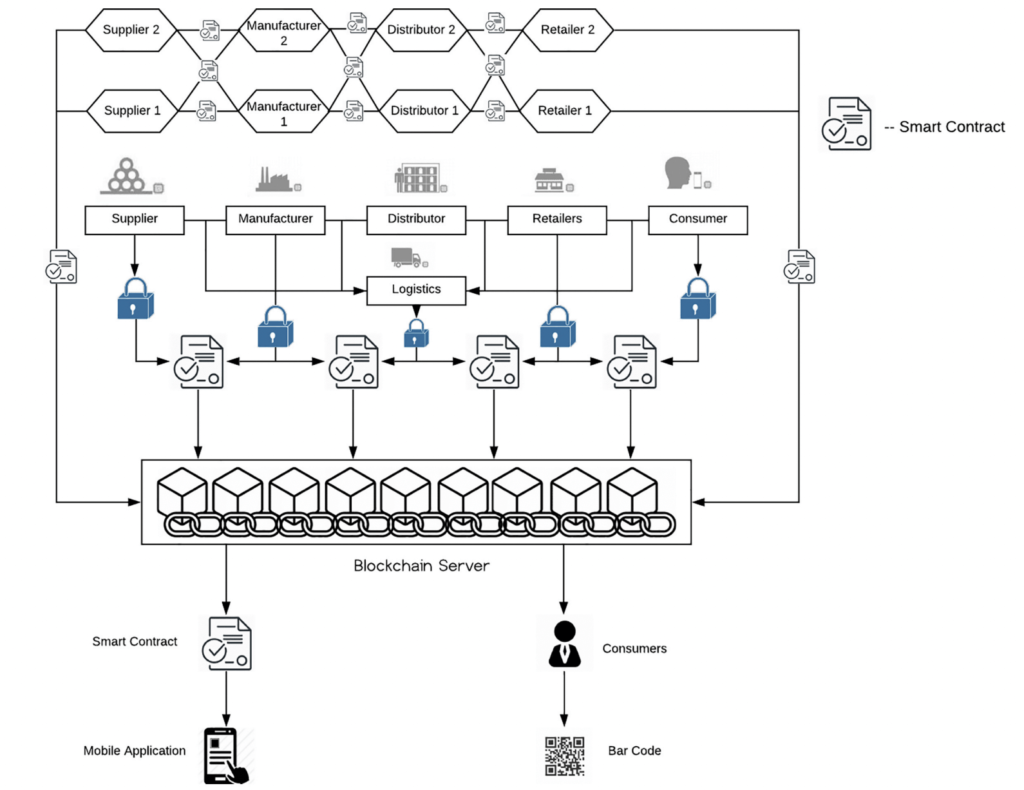
In the blockchain supply chain, AI can help with things like analyzing order data, keeping track of information stored on the blockchain, making financial decisions, and a lot more. This makes the data more open and safe.
Yet, advancements in AI are still in their infancy.
3-Integration of IoT with Blockchain Technology
Multiple blockchain platforms exist, some of which are designed specifically for Internet of Things (IoT) applications like Libra, IoT Chain, Atonomi, and Hydrachain. But these Internet of Things applications are still in their infancy. It is still exciting to see how IoT produces real-world benchmarks.
The following trends in the Internet of Things and blockchain could provide solutions.
-
Big Data
With the rise of IoT-connected devices, there is a growing interest in real-time data processing. A business may find great value in this data despite its complexity and volume. By analyzing IoT big data, researchers may be able to uncover insights that will greatly help users make better decisions.
Integrating big data with blockchain ledgers is a popular topic of discussion. For example, to allow quicker, cheaper, and more secure cross-account transactions, over 40 Japanese financial institutions have struck a deal with Ripple (which offers crypto solutions).
Yet the major obstacle is big data’s early stages.
-
Multi-level IoT Blockchain system
Due to its distributed ledger and consensus method, blockchain technology ensures integrity and consistency. However, this requires a powerful consensus algorithm and a lot of space on the existing blockchain. For this reason, an edge node, which is hosted in the cloud, manages the blockchain nodes used for IoT data integration.
Because blockchain has low computational power, there is no way to make sure that IoT data stored on it is secure, and the current centralized structure is still open to attacks. Researchers have proposed a multi-tiered blockchain architecture and consensus mechanism to address this weakness.
In the IoT chain, the multi-level blockchain system includes the following components:
- Export consensus method between the two blockchains,
- Schnorr signature method
- Random-based lightweight consensus algorithm
4: Enhance the storage space on the blockchain
The main challenge of combining the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain is keeping track of many copies of the same transaction across a network of nodes. There are, however, two options presented for dealing with this issue.
- Edge computing
- Software-defined networking (SDN)
When a transaction is made, a copy of the data is sent to all of the nodes in the blockchain system. Nodes are further linked to the SDN edge that provides additional storage space. This paves the way for a distributed network in which nodes can make verification judgments based on past transactions even if they do not trust one another. It’s a safer and more private option. SDN can also keep track of and look at data from every node in a blockchain network system.
Although this solution is good, it still lacks high-end computing standards.
5-Regulation and standardization of blockchain
The emergence of blockchain technology in cryptocurrencies is weakening the financial might of nation-states. As a result, there will be an imbalance in the flow of money, and 51% of blockchain minors will soon control more than 50% of all blockchain assets.
So, if a whole country wants to use cryptocurrencies as its official currency, they should be owned by the government. The best option is to keep cryptocurrencies on a national level with appropriate standards for now, and then bring them to a global level with universal standards for later.
Conclusion and limitations
It usually takes a long time for technological advances to develop into a stable, acceptable form that can be released to the market. Over the next few years, blockchain adoption will resemble that of other technologies. Despite the abundance of opportunities, it will require some effort to overcome the obstacles and fully realize its potential.
Even though the world is trying to find many ways to make it work better, the solutions themselves are not perfect. Moreover, it appears that combining with other technologies is inefficient as well since those technologies are still in their infancy. So, there’s a long way to go, but we’re not giving up hope.






Leave a Comment